Abrasion standards and test methods
Abrasion – quality standards
There are two internationally recognised sets of standards for abrasion, EN ISO 14890 (H, D, and L) and DIN 22102 (Y, W, and X). The longer-established DIN standards are most commonly used in Europe. Generally speaking, DIN Y (ISO 14890 L) relates to ‘normal’ service conditions and DIN W (ISO 14890 D) for particularly high levels of abrasive wear. However, DIN X (ISO 14890 H) is widely regarded as the most versatile because in addition to resisting abrasive wear it also has good resistance to cutting, impact (from high drop heights) and gouging, usually caused by heavy, sharp materials.
Abrasion – testing
The test method for abrasion (ISO 4649 / DIN 53516) is actually quite simple. Abrasion resistance is measured by moving a test piece of rubber across the surface of an abrasive sheet mounted on a revolving drum. It is expressed as volume loss in cubic millimeters, for instance, 150 mm³.
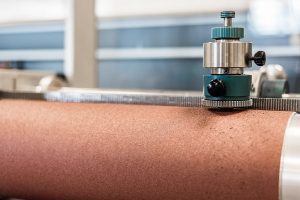

ISO 4649 / DIN 53516 abrasion testing
The most important thing to remember when looking at abrasion test results is that higher figures represent a greater loss of surface rubber which means that there is a lower resistance to abrasion. Conversely, the lower the figure the better the wear resistance. A single belt with good abrasion resistance can often run for longer than two or even three lower grade ‘economy’ belts.
SPECIAL NOTE: When assessing and comparing supplier data concerning abrasion (wear) resistance the performance tested data is often a better indicator than the actual cover grade itself. For example, standard Dunlop RA cover compound exceeds the requirement of DIN X but is significantly lower in cost.
